Lawsuits are formal legal actions brought before a court to resolve disputes or seek justice. They encompass a wide range of areas within the law, each addressing specific issues and legalities. Whether you’re seeking redress for a personal injury, breach of contract, or civil rights violation, understanding the different areas of law and the nature of common lawsuits can help you navigate the legal system effectively.
Understanding Lawsuits: Types, Common Cases, and Compensation
Lawsuits can fall under various legal categories, each governed by distinct rules and principles. Some of the primary areas of law include:
Personal Injury Law: Personal injury law deals with cases where an individual has been harmed due to another party’s negligence or intentional actions. Common cases include car accidents, slip and fall incidents, medical malpractice, and product liability.
Family Law: Family law addresses issues related to familial relationships. This includes divorce, child custody, child support, alimony, adoption, and paternity disputes.
Employment Law: Employment law covers disputes between employers and employees. Common lawsuits involve wrongful termination, discrimination, harassment, wage and hour disputes, and breach of employment contracts.
Contract Law: Contract law governs agreements between parties. Breach of contract cases arise when one party fails to fulfill their contractual obligations, leading to financial losses or other damages for the other party.
Property Law: Property law deals with disputes related to real estate and personal property. This includes landlord-tenant disputes, property damage, zoning issues, and eminent domain cases.
Civil Rights Law: Civil rights law involves cases where an individual’s constitutional rights have been violated. This includes discrimination based on race, gender, religion, or disability, as well as police misconduct and freedom of speech issues.
Business Law: Business law encompasses a wide range of legal issues faced by businesses. This includes partnership disputes, intellectual property issues, mergers and acquisitions, and antitrust cases.
Most Common Lawsuits
Certain types of lawsuits are more prevalent due to the nature of human interactions and societal structures. Some of the most common lawsuits include:
Personal Injury Claims: Personal injury claims are among the most frequent lawsuits. These cases arise from accidents or intentional acts that result in injury or harm to an individual. Common examples include car accidents, slip and fall cases, medical malpractice, and defective products.
Divorce and Family Law Disputes: Divorce and family law disputes are also common. These cases involve the dissolution of marriages, child custody battles, child and spousal support issues, and property division.
Employment Disputes: Employment disputes often lead to lawsuits, particularly in cases of wrongful termination, workplace discrimination, harassment, and wage and hour violations.
Breach of Contract: Breach of contract cases occur when one party fails to meet their obligations under a contract. This can happen in various contexts, including business agreements, real estate transactions, and service contracts.
Property Disputes: Property disputes can arise from landlord-tenant disagreements, property damage, boundary issues, and zoning conflicts.
Civil Rights Violations: Civil rights violations, including discrimination and police misconduct, often lead to lawsuits seeking to protect individuals’ constitutional rights.

Range of Compensation
The compensation awarded in lawsuits varies widely based on the type of case, the extent of damages, and the jurisdiction. Some common forms of compensation include:
Economic Damages: Economic damages are intended to compensate the plaintiff for financial losses. This includes medical expenses, lost wages, property damage, and other out-of-pocket costs.
Non-Economic Damages: Non-economic damages compensate for non-monetary losses, such as pain and suffering, emotional distress, loss of enjoyment of life, and loss of consortium.
Punitive Damages: Punitive damages are awarded in cases where the defendant’s conduct was particularly egregious or malicious. These damages are intended to punish the defendant and deter similar behavior in the future.
Specific Performance: In contract law, specific performance may be ordered, requiring the breaching party to fulfill their obligations under the contract rather than paying monetary damages.
Injunctive Relief: Injunctive relief involves a court order requiring a party to take specific actions or refrain from certain activities. This is common in cases involving property disputes or civil rights violations.
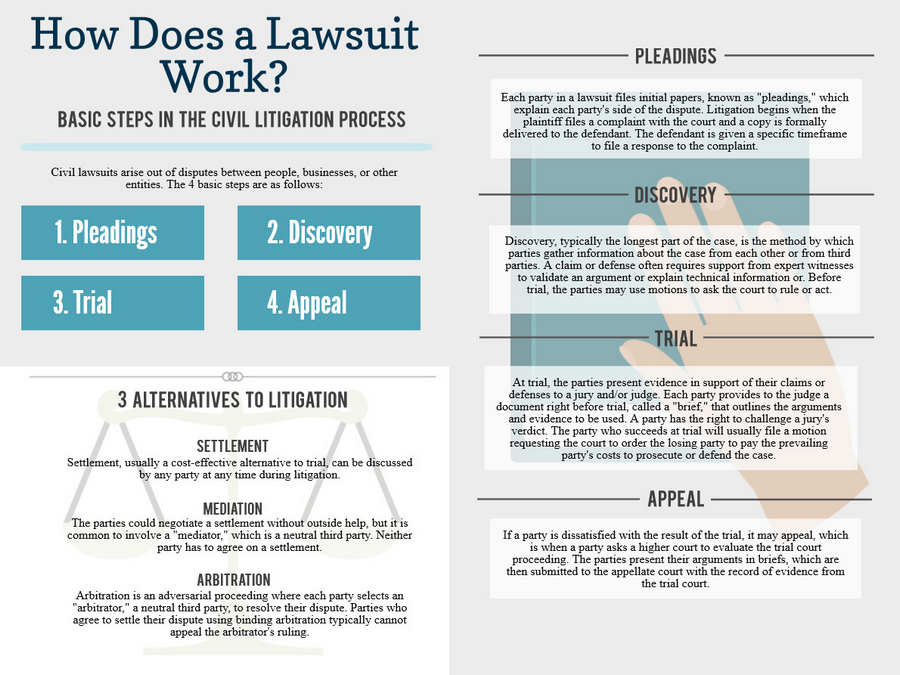
8 Step Overview To Filing A Lawsuit
Filing a lawsuit can be a daunting task, but it doesn’t have to be. Knowing the steps to take and the documents you need to file can make the process much easier. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to file a lawsuit.
Step 1: Determine Your Legal Claim
The first step in filing a lawsuit is to determine your legal claim. This means understanding the facts of your case and researching the applicable laws. You should also consider whether you have a valid legal claim and if it is worth pursuing.
Step 2: Choose the Right Court
Once you have determined your legal claim, you need to decide which court is the right one for your case. This will depend on the type of case and the jurisdiction in which it is being filed. You should also consider the cost of filing in a particular court and whether it is the most appropriate venue for your case.
Step 3: Prepare the Complaint
The next step is to prepare the complaint, which is a document that outlines your legal claim and the facts of your case. The complaint should include all relevant information, such as the names of parties involved, the facts of the case, and the legal claims you are making.
Step 4: File the Complaint
Once you have prepared the complaint, you need to file it with the court. This involves submitting a copy of the complaint to the court clerk and paying any applicable filing fees.
Step 5: Serve the Complaint
Once the complaint has been filed, you need to serve it on the other party. This involves delivering a copy of the complaint to the other party or their attorney. Depending on your jurisdiction, there may be specific rules for how this must be done.
Step 6: Respond to the Complaint
Once the complaint has been served, the other party must respond. This involves filing an answer to the complaint with the court. The answer should include any defenses or counterclaims that the other party may have.
Step 7: Prepare for Trial
Once the answer has been filed, you should begin preparing for trial. This involves gathering evidence, interviewing witnesses, and researching the applicable laws. You should also consider whether you need to hire an attorney to represent you in court.
Step 8: Attend Trial
Finally, you will need to attend the trial. This involves presenting your case to the judge or jury and arguing your legal claims. Depending on the outcome of the trial, you may be awarded damages or other relief.
Filing a lawsuit can be a complicated process, but it doesn’t have to be.
Lawsuits are a critical mechanism for resolving disputes and seeking justice across various areas of law. Understanding the different types of lawsuits, the nature of common cases, and the range of potential compensation can help individuals and businesses navigate the legal system effectively. Whether you are pursuing a personal injury claim, addressing a family law dispute, or defending your civil rights, having a clear understanding of the legal landscape is essential for achieving a fair and just outcome. By following these steps and understanding the documents you need to file, you can make the process much easier. If you need additional help or information, feel free to browse the law firm directory.
Featured Law Firms


